In case you have multiple environments and networks but you still would like to manage Prometheus monitoring from one central location, one option is to set up Federation. Federation allows a Prometheus server to scrape selected time series from another Prometheus server. This is basically a master and slave configuration where the slave is acting like a beefed up exporter, exposing data from all the exporters in the network where it is located.
Architecture
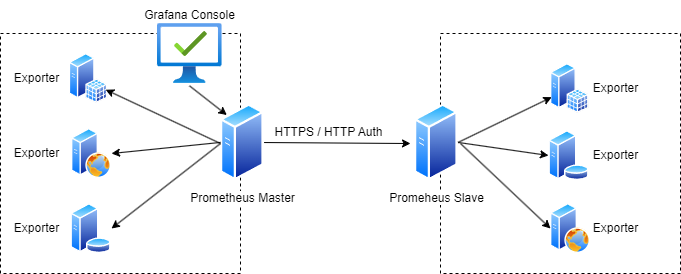
In this example scenario we have 2 Prometheus servers where the Prometheus Master is scraping information from not only the exporters in its own network but from the Prometheus slave server too over HTTPS and using HTTP Authentication.
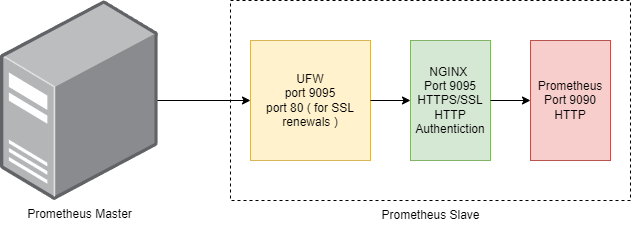
Prometheus doesn’t have any built in authentication nor can it use SSL certificates. We used NGINX proxying to achieve https communication and http url authentication along with local firewall settings.
Implementation
We assume that the Master Prometheus server is already installed and working correctly with the local exporters along with visualization using Grafana. In this implementation example we will focus on setting up the Slave Prometheus and to change the configuration of the Master Prometheus to enabled federation.
We used an aws t3.micro instance for the Slave Prometheus server. Once the OS is set up we will perform the following steps:
- Set up firewall rules.
- Set up Nginx and Certbot.
- Set up SSL Certificates.
- Create http password
- Configure Nginx.
- Set up and configure Slave Prometheus Server.
- Configure Master Prometheus Server.
Set up Firewall Rules
We use ufw to configure the local Ubuntu firewall. We will need to open the following ports:
- 9095 – This will be the SSL port for the Slave Prometheus Server.
- 80 – This is required by certbot to run its own webserver when it tries to auto-renew the certficiates.
- 22 – SSH port.
Since ufw is available on the ubuntu image we are using, all we have to do is to run the relevant commands to configure the ports. We would only want the Master Prometheus server to access port 9095 so replace x.x.x.x with the external ip of your Master Prometheus server.
sudo ufw allow from x.x.x.x proto tcp to any port 9095/tcp sudo ufw allow 80/tcp sudo ufw allow 22/tcp sudo ufw enable
Set up Nginx and Certbot
The next step is to install NGINX web server and certbot which will generate the certificates for us. We will also need to install apache2-utils to be able set the http auth password later.
sudo apt install nginx apache2-utils -y sudo snap install --classic certbot sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
Create HTTP password
In this step we will create the user and password for the http authentication. Let use prometheus-admin as username. Specify a password of your choice when prompted.
sudo htpasswd -ci /etc/nginx/.htpasswd prometheus-admin
This command creates the /etc/nginx/.htpasswd file which will contain the username and password ( in encrypted format ). These credentials will be used for the Prometheus Master to connect to the Prometheus Slave.
Set up SSL Certificates
We will use certbot now to create the SSL certfificates. The prerequisite for this process is that the hostname of the Prometheus Slave is DNS resolvable. Let’s say the resolvable name of our server is prometheus-slave.example.com we will use this throughout the example.
sudo certbot certonly --standalone --noninteractive --agree-tos --cert-name prometheus-slave -d prometheus-slave.example.com -m info@example.com -v
This will create the certificates for you in the /etc/letsencrypt/live/prometheus-slave directory.
Add the following to your crontab, this command will try to renew the certificates automatically every 12 hours and restarts the nginx server when it runs successfully.
0 */12 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quiet && /usr/bin/systemctl restart nginx
Configure Nginx
We will now create the nginx.config file. Create the file into a directory location of your choice.
server {
listen 9095 ssl;
server_name prometheus-slave.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/prometheus-slave/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/prometheus-slave/privkey.pem;
ssl_dhparam /snap/certbot/current/lib/python3.8/site-packages/certbot/ssl-dhparams.pem;
location / {
auth_basic "Prometheus Slave";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
proxy_pass http://localhost:9090;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
Now we need to copy and enable the configuration on nginx. We will also delete the default nginx configuration. Execute this command sequence from the location where you created the nginx.config file.
sudo service nginx stop sudo cp ./nginx.config /etc/nginx/sites-available/nginx.config sudo rm -rf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nginx.config sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/nginx.config /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/nginx.config sudo rm -rf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default sudo service nginx start
Set up and configure Slave Prometheus Server
The next step is to download and set up Prometheus on the Prometheus Slave server. The following steps will be followed:
- Create the Prometheus user.
- Download the latest Prometheus version.
- Copy the files to binary directory.
- Edit the prometheus.yaml file to start scraping your local exporters.
- Enable Prometheus linux service and start operating the product
We now create the Prometheus user.
sudo useradd --system --no-create-home --shell /bin/false prometheus
We now use the following script to download the latest Prometheus version from github.
#!/bin/bash
ARCH="linux-amd64"
GITHUB_URL="https://api.github.com/repos/prometheus/prometheus/releases/latest"
RELEASE_DATA=$(curl -s $GITHUB_URL)
VERSION=$(echo $RELEASE_DATA | grep -oP '"tag_name": "\K(.*?)(?=")')
ASSETS_URL=$(echo $RELEASE_DATA | grep -oP '"browser_download_url": "\K(.*?)(?=")' | grep "$ARCH.tar.gz")
if [[ -z "$VERSION" ]] || [[ -z "$ASSETS_URL" ]]; then
echo "Failed to find the latest Prometheus version or the download URL."
exit 1
fi
wget "$ASSETS_URL" -O prometheus-${VERSION}-${ARCH}.tar.gz || curl -L "$ASSETS_URL" -o prometheus-${VERSION}-${ARCH}.tar.gz
echo "Extracting Prometheus $VERSION..."
tar xvf prometheus-${VERSION}-${ARCH}.tar.gz
We now have the latest Prometheus version downloaded and extracted. Let’s move the files to their final location and create the required directories. Run the following command sequence from the same directory where the prometheus files have been extracted.
export DIRNAME=$(find . -type d -name "prometheus*" -print -quit) cd $DIRNAME sudo mkdir -p /data /etc/prometheus sudo mv prometheus promtool /usr/local/bin/ sudo mv consoles/ console_libraries/ /etc/prometheus/ sudo mv prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/ /data/
Edit the /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml file and add your local exporters. As an example we add a job with the name of CoreSystems and add 4 targets to the group. We use the internal ip address and hostname for the targets so scraping traffic is only happening on the internal network. You would typically have to append each job definition at to end of the file.
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Alertmanager configuration
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
# - alertmanager:9093
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global 'evaluation_interval'.
rule_files:
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
# -------------------------
# Custom targets and groups start here
# --------------------------
- job_name: 'CoreSystems'
static_configs:
- targets: ['core01.example.internal:9100']
- targets: ['core02.example.internal:9100']
- targets: ['core03.example.internal:9100']
- targets: ['core04.example.internal:9100']
labels:
group: 'CoreSystems Monitoring'
Check the syntax if the configuration file.
sudo /usr/local/bin/promtool check config /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Create a linux service file called prometheus.service using the following example.
[Unit] Description=Prometheus Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target StartLimitIntervalSec=500 StartLimitBurst=5 [Service] User=prometheus Group=prometheus Type=simple Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5s ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \ --config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ --storage.tsdb.path=/data \ --web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \ --web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries \ --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9090 \ --web.enable-lifecycle [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Run the commands below from the directory where you created the service file. This will create the prometheus linux service, enable it to autostart at reboot and at the same time will start the service.
sudo cp prometheus.service /etc/systemd/system/ sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable prometheus sudo systemctl start prometheus sudo systemctl status prometheus
Your Prometheus Slave server is now set up.
Configure Master Prometheus Server
As the Prometheus Master Server has already been set up all we need to do is to add a new job at the end of the /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yaml file to enable scraping from the Prometheus Slave Server. Very likely you already have some other jobs configured in that configuration file, you do not need to remove them, they will be compatible with the federated setup. Change the user and the password at the bottom of the file to whatever you are used at the http credentials setup.
This configuration will scrape everything that is available on the Slave Prometheus Server. if you only need to scrape specific data you can set that up at the params section.
- job_name: 'federate'
scrape_interval: 15s
honor_labels: true
metrics_path: '/federate'
params:
'match[]':
- '{__name__=~".+"}'
static_configs:
- targets: ['prometheus-slave.example.com:9095']
scheme: https
basic_auth:
username: 'prometheus-admin'
password: 'YOUR PASSWORD'
Once you have appended the above to the end of your /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yaml file, run the following to check and reload the configuration.
sudo /usr/local/bin/promtool check config /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml curl -X POST http://localhost:9090/-/reload
Your federated Prometheus servers are now set up.